+62 817-4929-054
Knowing the Spinal Cord, Its Functions, and Disorders
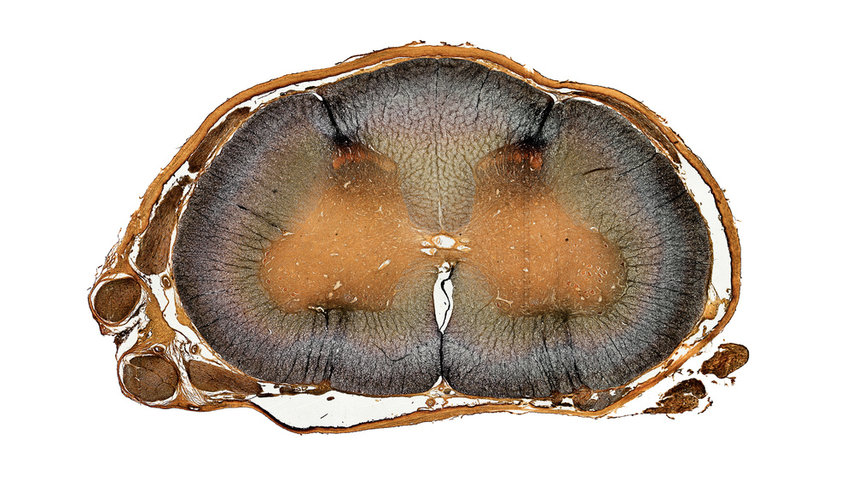
Spinal cord or the spinal cord is a long, tube-like network that connects from the brain to the lower back. This organ carries nerve signals from the brain to the body and vice versa, resulting in damage whatever in the spinal cord will affect the movement or function of other body organs.
Spinal Cord Anatomy
The length of the spinal cord varies from person to person. However, medical experts estimate that women have a spinal cord that is 43 cm long, while men have about 45 cm.
The spinal cord is divided into 3 parts, namely cervical (neck), thoracic (chest), and lumbar (lower back). This organ is also protected by 3 layers of tissue: dura mater, arachnoid mater, And pia mater Doctors usually call these three layers “meninges,”. Here is the explanation:
- Dura mater: outermost layer meninges spinal cord. This layer has a strong texture.
- Arachnoid mater: the middle layer covering the spinal cord.
- Pia feeds: the deepest layer of (which is in direct contact with) the spinal cord.
Between the three layers of tissue above, there is also a space that becomes a "pathway" for organ fluids. Between dura mater And arachnoid mater, for example, there is epidural space (epidural space) which is where the doctor administers local anesthesia to reduce pain during childbirth or surgical procedures such as lung aneurysms or stomach aneurysms.
While in between arachnoid mater And pia mater there is subarachnoid space (subarachnoid space) which is where the cerebrospinal fluid (SCF) is also located to inject local anesthesia for surgery caesar or knee replacement.
Spinal Cord Function
The main function of the spinal cord is to carry nerve signals throughout the body. In detail, the signals or messages carried by these nerves have three important tasks for the human body, namely:
- Carries signals from the brain. Signals sent by the brain through the spinal cord will control every human movement. Apart from that, these signals are also responsible for directing the body's autonomic (involuntary) functions, such as respiratory rate, heart rate, bowel function, and bladder function.
- Carries information to the brain. Signals from parts of the body that pass through the spinal cord nerves can also send messages back to the brain. Examples are the sensations of touch, pressure, and pain.
- Manages body reflexes. The spinal cord is also able to function independently (without involving the brain) in controlling motor reflexes. For example, the spinal cord manages reflexes patela, which is a reflex when someone moves their leg accidentally when their shin or knee is tapped by another person.
Spinal Cord Abnormalities
The spinal cord is a sensitive part of the body. When the body experiences injury or disturbance, this organ is very likely to be affected. Not only that, injuries or abnormalities to the spinal cord are also usually serious and can cause severe symptoms in the surrounding body parts.
The following are several conditions that can cause abnormalities in the spinal cord:
- Acute transverse myelitis. Inflammation of one or more spinal segments.
- Cervical spondylosis. Progressive (continuous) wear of the spinal discs in the neck (cervical disks) which can compress the spinal cord.
- Herniated disks. Displacement of spinal discs from their place into the space around the spinal cord, thereby pressing on the surrounding nerves.
- Spinal fractures. Spinal fracture or condition when one or more vertebrae are pinched or broken and press on the spinal cord.
- Spinal muscular atrophy. A rare genetic condition that causes a person to lose motor nerve cells in the spinal cord. The result is weakness and muscle wasting.
- Spinal stenosis. Narrowing of the spine resulting in pinched nerves and irritation of the spinal cord.
- Spinal tumors. Spinal tumor or swelling of body tissue (cancerous or not) that starts in the spine and eventually presses on the spinal cord.
- Spinal infections. Spinal infection is a condition when an abscess (inflammation of body tissue) spreads widely, the spine collapses (weakens), or an infected disc presses on the spinal cord.
The important role of the spinal cord for survival means that every individual needs to maintain the health of this body organ properly. In this way, risks such as abnormalities that might disrupt the condition of the spinal cord and overall body performance can be avoided.
You can also visit the Spine Center at Premier Bintaro Hospital for consultations regarding health or spinal cord disorders. spine treatment, and other problems related to the spine.
The integrated and comprehensive Spine Center service center at Premier Bintaro Hospital is handled by various specialist doctors, starting from Spine Orthopedic Specialist Doctors, but also by Neurology Specialist Doctors, Neurophysiology Specialist Doctors, Medical Rehabilitation Specialist Doctors, and Radiology Specialist Doctors. These doctors can also perform non-operative and operative spinal treatment procedures.
For information and to make an appointment, contact us at:
- RS Premier Hospitals Careline: 1 500 908
- WhatsApp Chatbot Appointment: +62 8122 2309 911
Contact Us
For information and to make appointment

















